洗牙保健
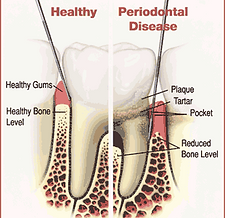
Periodontal diseases can affect one or more of the periodontal tissues/structures (e.g. alveolar bone, periodontal ligament, cementum and gingiva). While there are many different periodontal diseases that can affect these tooth-supporting tissues/structures, by far the most common ones are plaque-induced inflammatory conditions, such as gingivitis and periodontitis. Often the term periodontal disease or gum disease is used as a synonym for periodontitis, specifically chronic periodontitis.

No bleeding or puffy gums, pocket all measure to a normal 3 mm or less
Bleeding gum when measured, puffy in appearance and pockets no greater than 3 mm.
Bleeding and puffy gums that measure slightly more than normal at up to 5 mm.
Bleeding and swollen gums with pockets that measure up to 6 mm and more. Recession beginning to appear.
When periodontitis progresses to the advanced stage, the gums severely recede.
There are a variety of treatments for gum disease depending on the stage of disease. Treatments range from nonsurgical therapies that control bacterial growth to surgery to restore supportive tissues.
Non-surgical treatment
-
Professional dental cleaning
-
Scaling and root planing
Surgical treatment
-
Flap surgery/Pocket reduction surgery
-
Bone grafts
-
Soft tissue grafts
-
Guided tissue regeneration
-
Bone surgery







